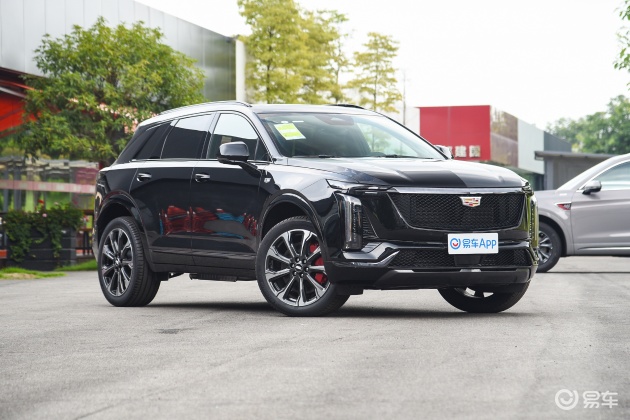
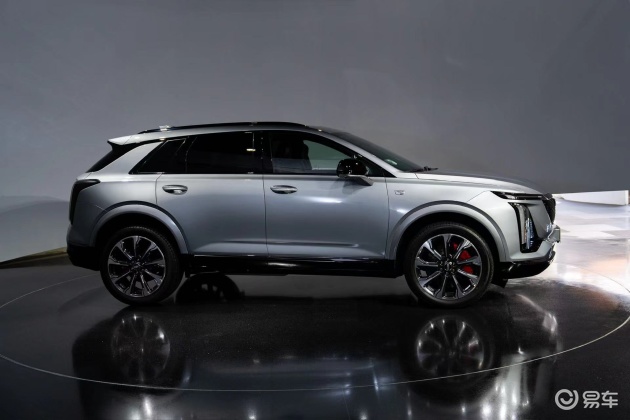
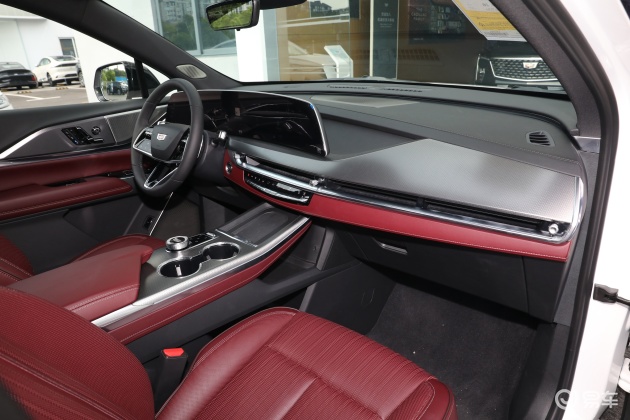
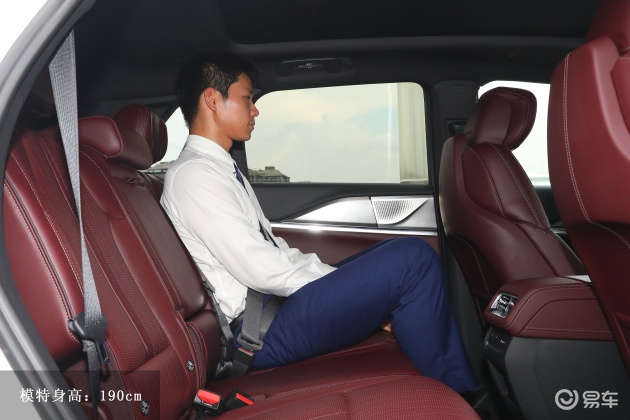
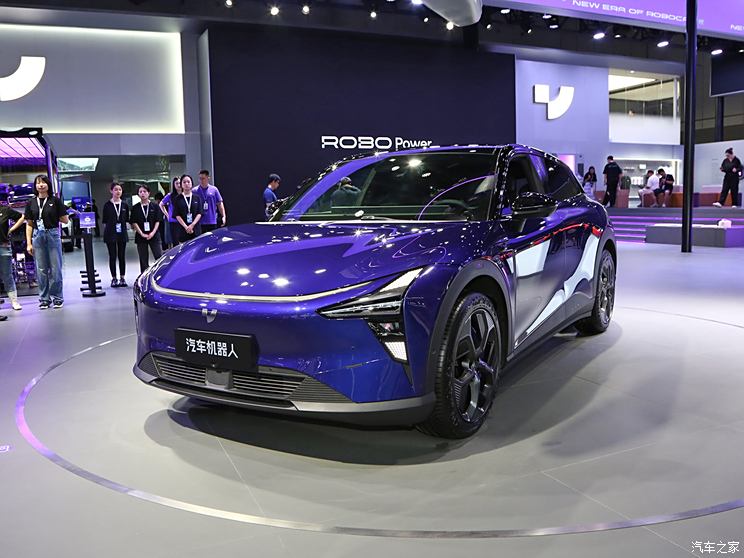
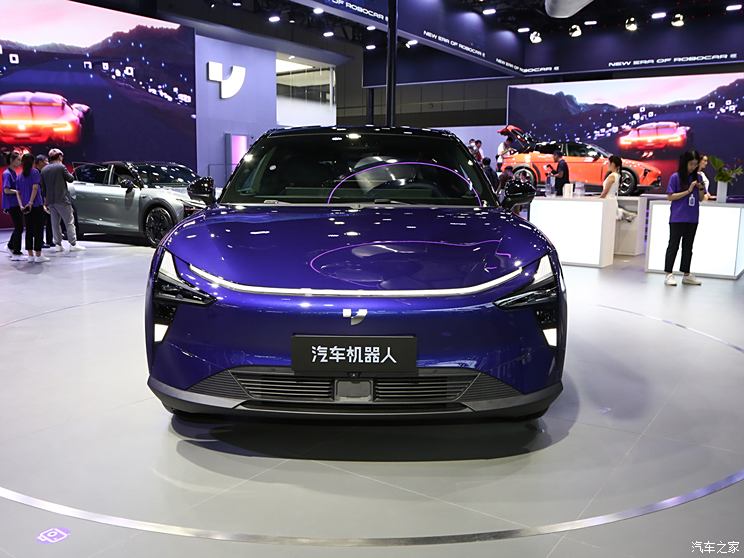
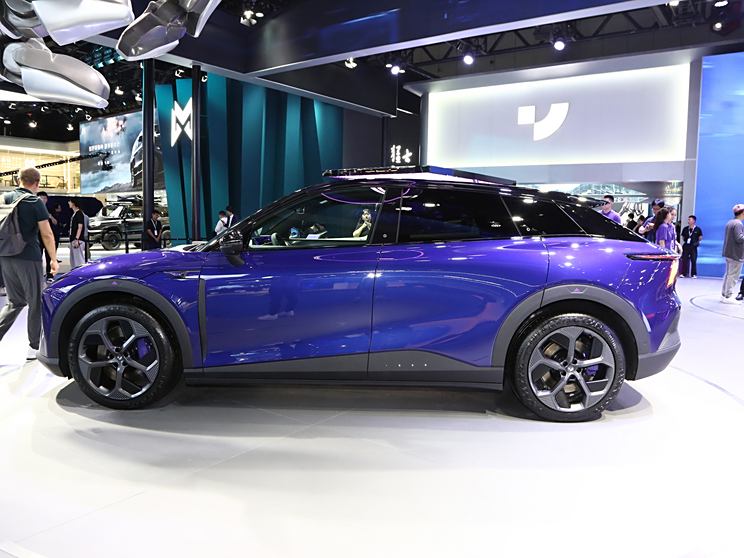
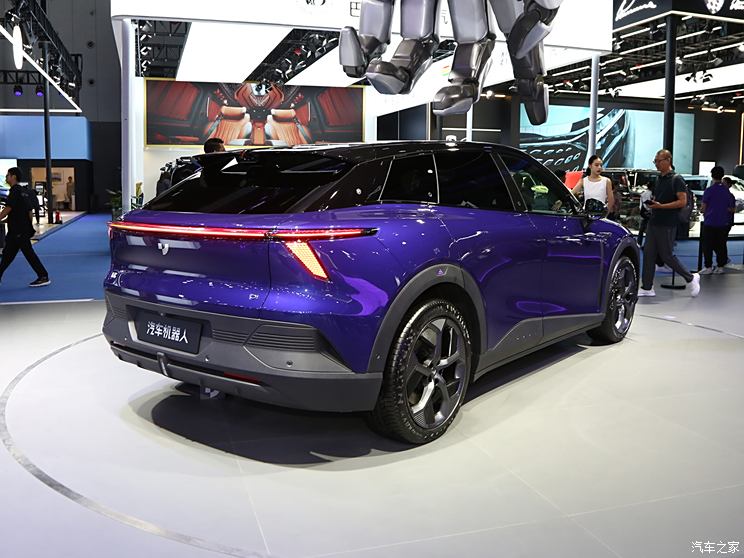
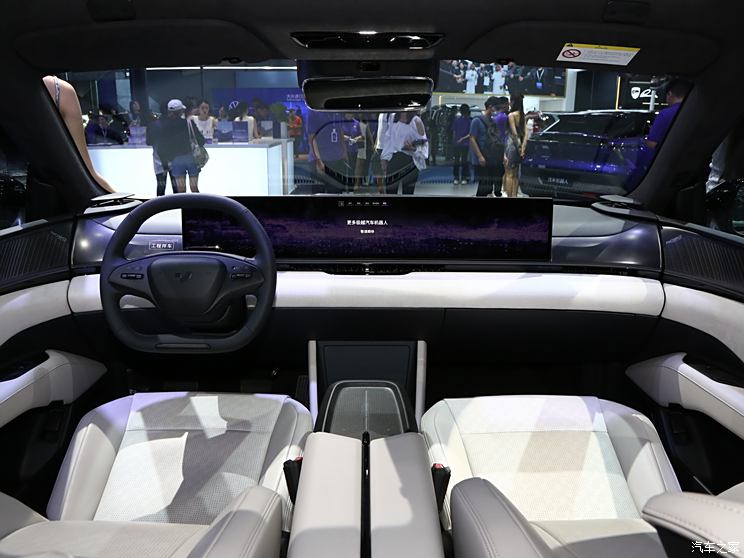
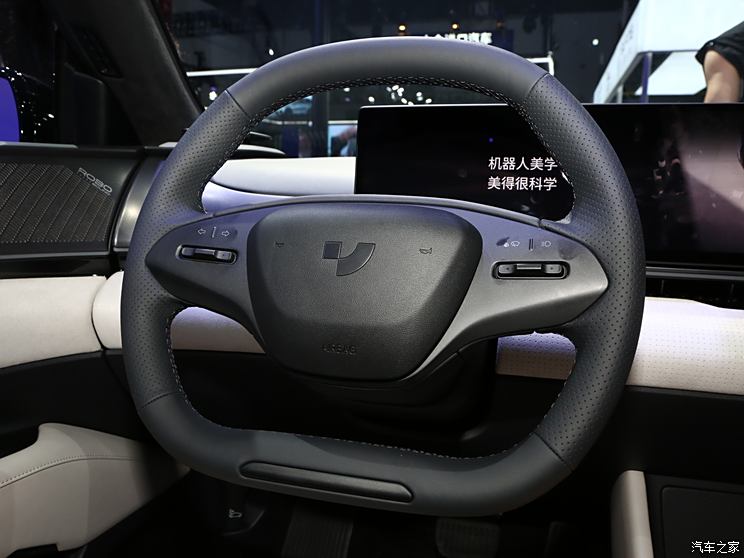
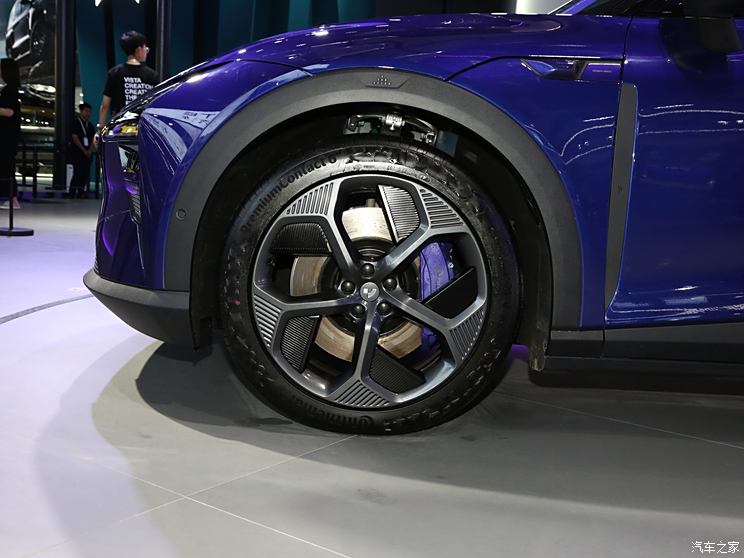
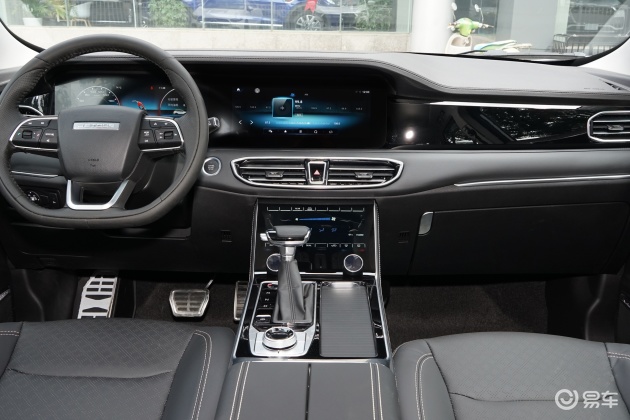
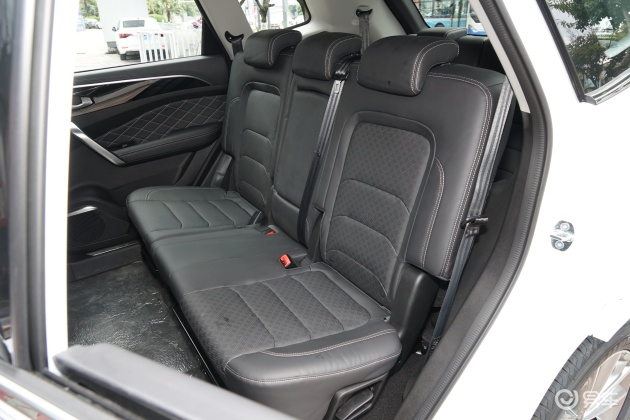
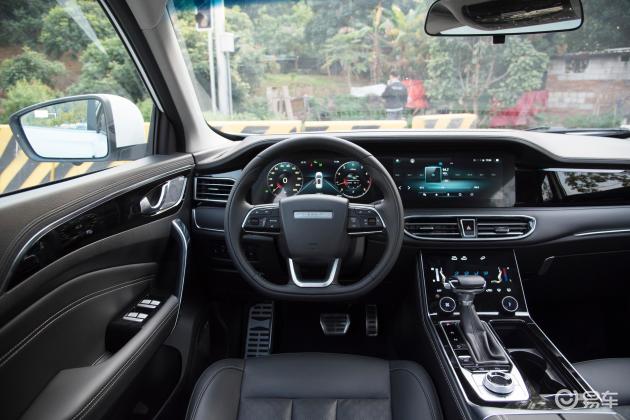
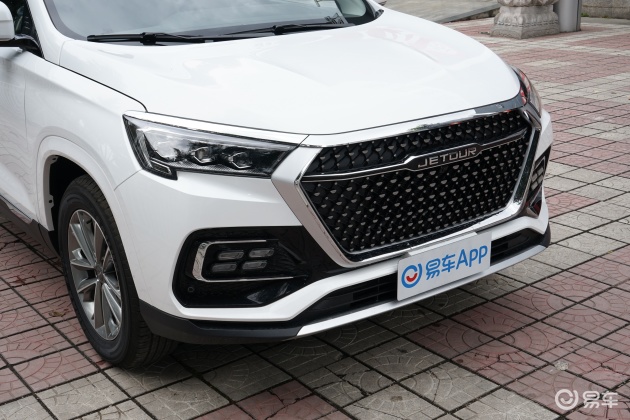
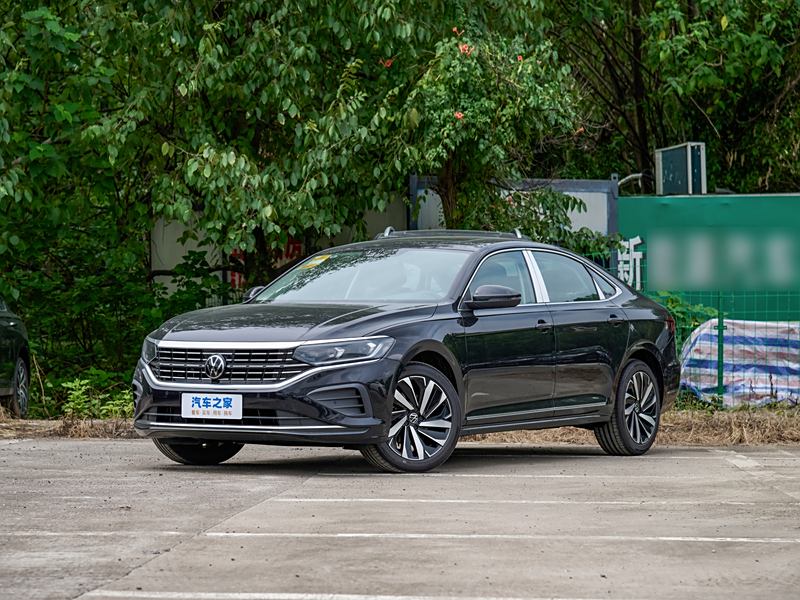
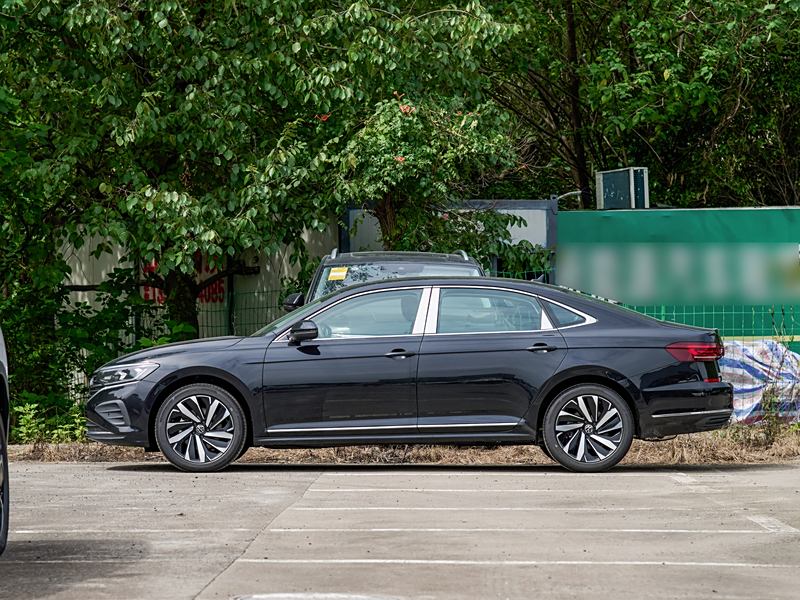
On the basis of the curtain call, [Car History] released the next generation development blueprint-Mazda. Although its launch does not mean that the next generation of mazda 6 is approaching, at least it shows us the figure of the next generation of mazda 6, and at the same time accelerates the research and development speed of the next generation of mazda 6. While this brand-new concept car is released, let’s take a look at what the course of mazda 6 is like.

Naming of mazda 6: Capella(616 618 626)/Atenza (mazda 6)
In the same way, in the decades of mazda 6’s development, it also adopted various naming methods, including Mazda 616, 618 and 626 and today’s mazda 6. In Japan, Mazda 616, 618 and 626 (before 2002) were named Capella, and mazda 6 after 2002 was named Atenza.
Research and Development Background of the First Generation mazda 6: Launched as a Mazda Global Strategic Model.
After the release of the first Mazda brand model Familia (the predecessor of Mazda 3) in 1960, Mazda brand entered a stage of rapid development. At that time, Familia series and Capella series were two important global strategic models in Mazda’s family tree. The former was built into a successful "family model" by Mazda, while the latter was put into production from 1970 to 2002, with a slightly higher positioning than Familia, and was mainly engaged in sports, and later transformed into an intermediate model.
● The First Generation Mazda Capella(616/618):1970-1974
Main sports:,
In May, 1970, the first generation of Mazda Capella was born in Japan. At the same time, in 1971, this model was introduced to overseas markets. In overseas, this model was called Mazda 616, and the last 16 represents that it adopted a 1.6L displacement. In the past, it adopted the power layout of front and rear drive, and it has two-door and four-door versions.


In terms of design, the first generation Capella has obvious American characteristics, and its slender body and rough style look like an authentic American car. It is precisely because of its very American shape that when Mazda introduced this model to the global market in 1971, it received very good results, including 63,389 vehicles sold in 1971, 57,748 vehicles sold in 1972 and 54,962 vehicles sold in 1973. In terms of body size, the length, width and height of the first generation Mazda 616 sedan version reached 4150mm, 1580mm and 1420mm respectively, which was 2470mm, equivalent to the size of the compact car now.


In terms of power carrying, in addition to the above-mentioned 1.6L engine with a maximum of 104 horsepower and a maximum of 144 Nm, in October 1970, Mazda also added a 1.5L engine with a maximum power of 78 horsepower and a maximum torque of 118 Nm. In 1971, Mazda also introduced a 1.8L 618 model to cater to the American automobile market which prefers large displacement. The maximum power of this engine is. However, this model did not get much recognition in the American market. In 1973, Mazda stopped selling Mazda 618, and after that, only its RX-2 with rotary engine was left in the American market. The engine is matched with 4 speeds.
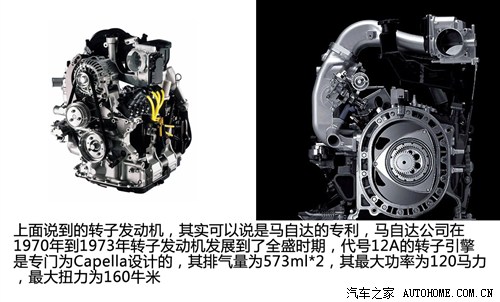
In fact, the rotor engine mentioned above can be said to be a patent of Mazda. Mazda, which is famous for its rotor engine, developed into its heyday from 1970 to 1973. Naturally, Mazda also introduced the Mazda Capella model with rotor engine. The rotary engine code 12A is specially designed for Capella. Its displacement is 573ml*2, its maximum power is 120 HP, and its maximum torque is 160 Nm. After being mounted on Mazda Capella, its maximum speed can reach 190 km/h, and it takes 15.7 seconds to complete the acceleration from 0 to 400 meters. Capella equipped with rotor engine is also exported to overseas markets including the United States, which is called Mazda RX-2.
""Click to view the development history of Mazda rotor series models ""
● The Second Generation Mazda Capella(616/618):1974-1978
Little change compared with the first generation/the development of rotary engine has entered a trough.
In February 1974, Mazda Capella ushered in a replacement. In fact, it is more appropriate to say that it is a big change than a replacement, because compared with the previous generation, the whole model has not changed much, but the front face of the appearance and the dashboard of the interior have been simply designed, while the power is still the rotor, 1.6L and 1.8L engines of the previous generation, and the 1.5L engine has been discontinued.


In terms of appearance change, the front face of the second-generation Mazda Capella has added more chrome decoration, and the lower bumper has also become a new design. In terms of vehicle size, only the length has increased by 110mm to 4260mm, and other dimensions have not changed. In addition, in the interior, the dashboard part is designed with four consecutive circles.
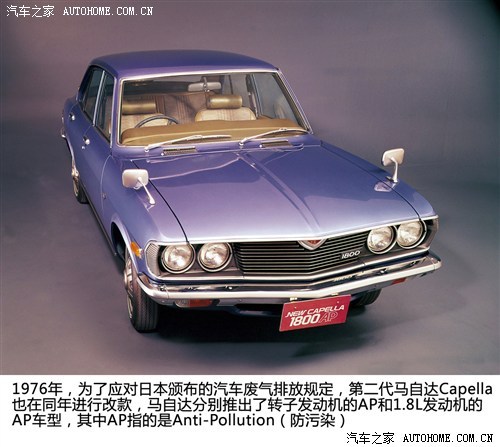

In 1976, in order to cope with the automobile exhaust emission regulations promulgated in the 51st year of Showa, Japan (1976), the second generation Mazda Capella also made changes in the same year, and introduced the AP models with rotary engine and 1.8L engine respectively, where AP means Anti-Pollution. In the nine years since the first and second generation Mazda Capella were launched, Capella has sold a total of 225,003 vehicles in Japan.

It is worth mentioning that after the heyday of Mazda’s rotary engine in 1973, Mazda, which originally intended to fully promote the rotary engine technology, encountered a global oil crisis in 1973. The shortage of gasoline supply made most car owners stay away from rotary engines (disadvantages of rotary engines: high fuel consumption and high manufacturing cost). Therefore, the sales performance of Mazda brand has entered an unprecedented low point. In 1977, Toyo Industry (the original company name of Mazda Automobile), which was caught in a business crisis, reorganized its corporate structure with the intervention of banking institutions. At the same time, Matsuda Gengping abdicated and Yamazaki Yoshiki took over as president.










































